Problem 2 A straight line on the surface of a sphere must curve from an extrinsic or external viewpoint, but intrinsically, say for example if we are living in Kansas, we can define what it means to feel like we are walking on a straight path. What is straight (intrinsically) on a sphere? Is the equator an intrinsically straight path? Is the non-equator latitude between Tallahassee, Florida and Multan, Pakistan an intrinsically straight path?
Problem 3 For thousands of years, people argued about the
necessity and validity of Euclid's Parallel Postulate.
One form of this postulate is given as
Playfair's Axiom:
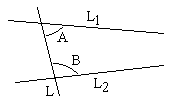
Through a given point, only one line can be drawn parallel to a given line.
Is this true on the sphere?
| Problem 4 Besides 23 definitions and several implicit assumptions, Euclid derived much of planar geometry from five postulates. For thousands of years, people argued about the necessity and validity of Euclid's 5th Postulate: If a straight line crossing two straight lines makes the interior angles on the same side less than two right angles, the two straight lines, if extended indefinitely, meet on that side on which are the angles less than the two right angles. Is this true on the sphere? |
 |
Problem 6 Is SAS (side-angle-side, which says that if 2 sides of a triangle and the angle between them are congruent to those in a corresponding triangle, then the 2 triangles must be congruent) always true for spherical triangles (a curved triangle formed by three shortest distance paths) on the surface of a perfectly round beach ball? Explain.
Problem 7 Assume that we have a right-angled spherical triangular plot of land (a curved triangle formed by three shortest distance paths on the surface of the sphere that also contains a 90 degree angle) on the surface of a spherical globe between approximately Umanak, Greenland, Goiania, Brazil, and Harare, Zimbabwe, that happens to measure 300 and 400 units on its short sides. Is the measurement of the long side from Greenland to Zimbabwe greater than, less than or equal to 500 units (ie is the Pythagorean Theorem true on the sphere)? Why?
Problem 8 On the surface of a perfectly round beach ball representing the earth, if we head 30 miles West, then 30 miles North, then 30 miles East, and then 30 miles South would we end up back where we started? Why? What about 300 miles in each direction? What about 3000 miles in each direction? Explain.
Problem 9 Is the surface of a sphere 2-dimensional or 3-dimensional? Why?
Problem 10
If we slice a perfectly round loaf of bread into equal
width slices, where width is defined as usual using a straight edge or ruler,
which piece has the most crust (or surface area)? Why?
Geometry of our Entire Universe
Problem 11 Is our universe 3-dimensional or is it
higher dimensional? Why?
Problem 12 Are there are finitely or infinitely many stars in the universe? Explain.
Problem 13 The geometry that you explored in high school is called Euclidean geometry. For example, you learned about the Euclidean law stating that the shortest distance path between two points is a straight line and about the Euclidean law stating that the sum of the angles in a triangle is 180 degrees. Is our universe Euclidean (ie does it satisfy the laws of Euclidean geometry such as those just mentioned)? How could we tell?
Problem 14 While people thought that the earth was flat for a long time, we know that the shape of the earth is actually a round sphere. What is the shape of space (the universe)?
Your Project 2 grade will be based on the quality of the web and/or book references that you find and/or experiments that you conduct, along with the clarity and depth of your answer. Having the "right" answer is not of prime importance as it is often the case that at this stage, mathematicians will still have incorrect ideas. The idea here is to deeply explore your question with help from web searching and/or experiments, and then to clearly communicate your research.